The United Arab Emirates (UAE) has long been recognized as a global business hub, offering entrepreneurs and corporations an attractive environment with minimal taxation. However, with the introduction of UAE Corporate Tax in 2023, businesses must now understand compliance requirements and plan their finances accordingly.
In this guide, we’ll break down the key features of UAE Corporate Tax, who it applies to, exemptions, filing obligations, and strategies for effective tax planning.
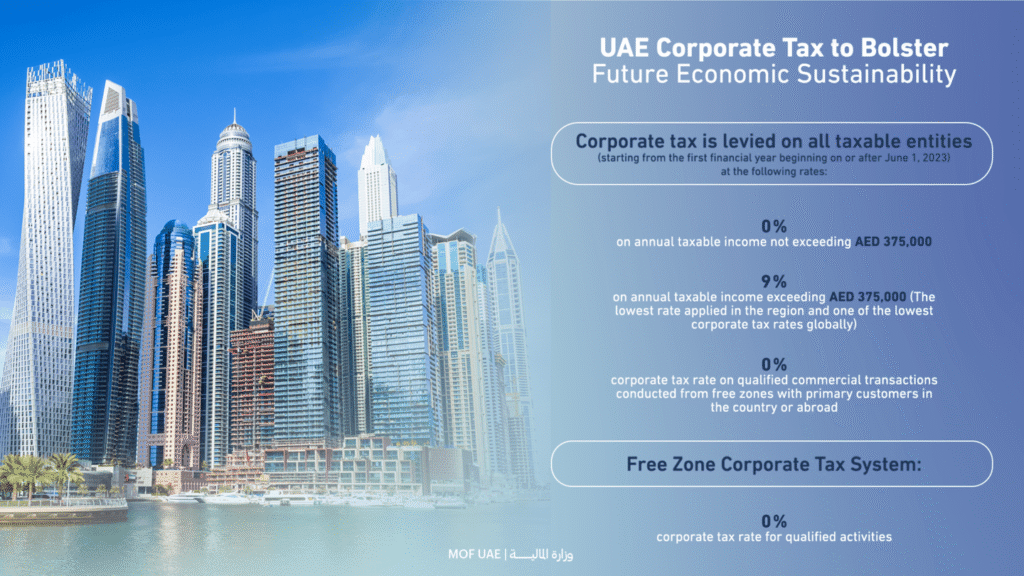
What is Corporate Tax in the UAE?
Corporate Tax, also referred to as business profit tax, is a direct tax imposed on the net income of companies. The UAE introduced it with the aim of:
- Aligning with international tax practices.
- Diversifying government revenue.
- Increasing financial transparency for investors.
The UAE’s Federal Decree-Law No. 47 of 2022 governs corporate taxation, marking a significant shift for businesses that have enjoyed decades of tax-free status.
Who is Subject to UAE Corporate Tax?
Corporate Tax in the UAE applies to:
- UAE-registered companies – including mainland and free zone entities (with certain exemptions).
- Foreign companies with permanent establishments in the UAE.
- Individuals conducting business activities under a commercial license.
UAE Corporate Tax Rates
The UAE has implemented one of the most competitive tax regimes in the world. The rates are structured as follows:
- 0% on taxable income up to AED 375,000 (to support small businesses and startups).
- 9% on taxable income above AED 375,000.
- 15% (potentially higher) for large multinationals that fall under OECD’s Pillar Two framework (companies with revenues exceeding EUR 750 million).
This tiered structure ensures the UAE remains a business-friendly jurisdiction while aligning with global tax reforms.
Exemptions from UAE Corporate Tax
Not all entities in the UAE are subject to corporate tax. The following remain exempt:
- Natural resources companies (oil and gas, extraction, etc.).
- Charitable organizations and public benefit entities.
- Investment funds (if they meet specified conditions).
- Government entities and wholly-owned government companies.
Free zone companies also benefit from preferential tax treatment if they comply with qualifying income rules, making them an attractive option for investors.
How to Calculate Corporate Tax in UAE
The taxable income is calculated based on the accounting net profit of the business as per international accounting standards, with adjustments for:
- Non-deductible expenses.
- Exempt income (like dividends from qualifying shareholdings).
- Transfer pricing rules.
For example:
If your company reports an annual net profit of AED 1,000,000, the calculation would be:
- 0% tax on AED 375,000.
- 9% tax on the remaining AED 625,000 = AED 56,250.
How to Prepare for UAE Corporate Tax
To remain compliant and tax-efficient, businesses should:
- Conduct a tax impact assessment of their financials.
- Review business structures (mainland vs free zone).
- Implement robust accounting and bookkeeping systems.
- Seek advice from tax advisors to minimize liabilities.
This is where professional financial services play a crucial role in ensuring compliance and optimizing tax strategies.
👉 Explore our Financial Services to learn how BlueHub Consultants can help you with bookkeeping, corporate tax advisory, and compliance solutions.
Why Professional Tax Advisory is Essential
Navigating UAE Corporate Tax requires in-depth knowledge of local regulations and international tax standards. Partnering with professional consultants ensures:
- Accurate tax filings.
- Avoidance of penalties.
- Strategic tax planning to maximize profits.
- Guidance on transfer pricing and international tax compliance.

